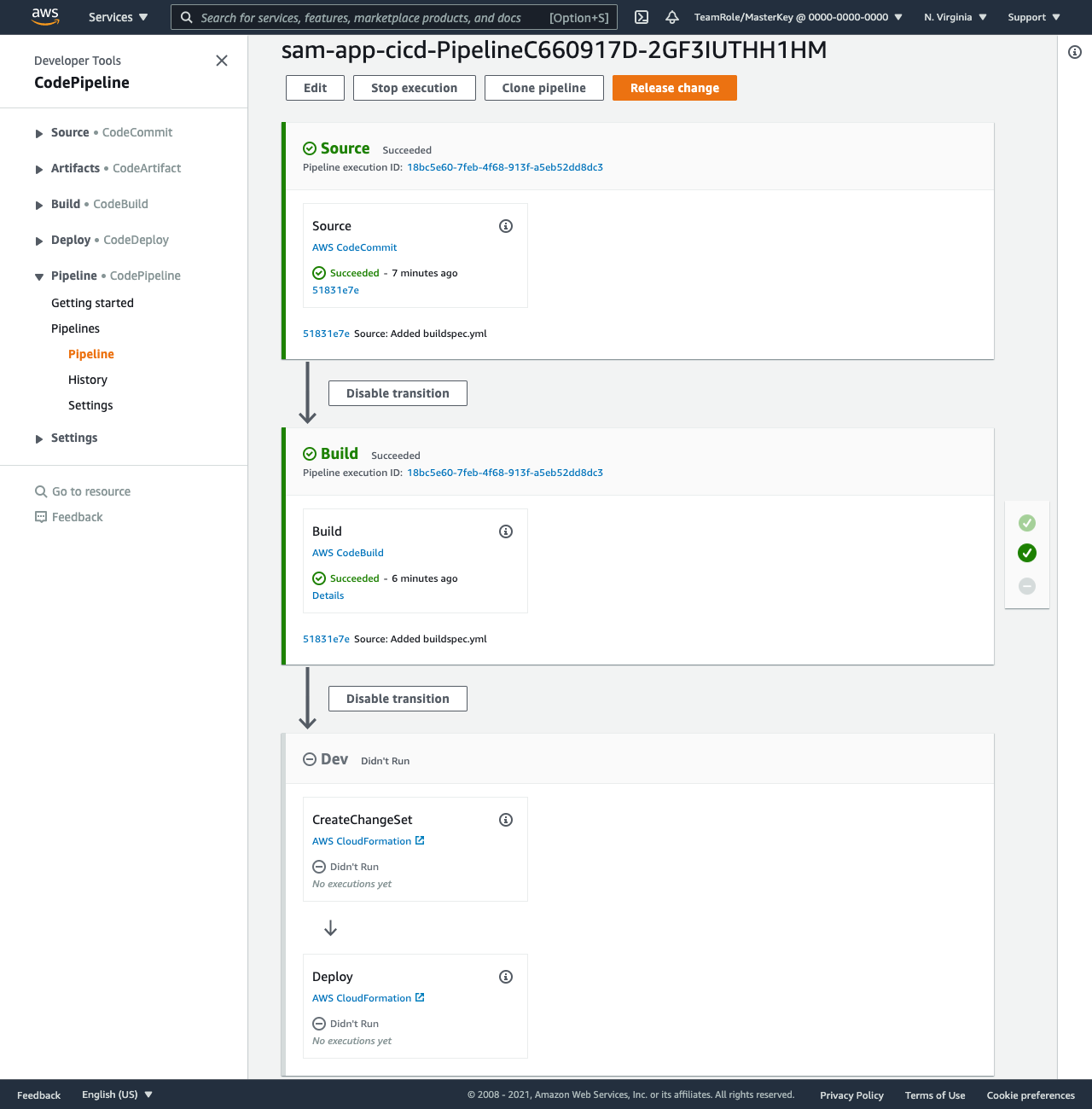
Deploy stage
The Deploy Stage is where your SAM application and all its resources are created an in an AWS account. The most common way to do this is by using CloudFormation changesets to deploy. This means that this stage will have two actions: the CreateChangeSet and the ExecuteChangeSet.
Add the Deploy stage to your pipeline_stack.py:
# Deploy stage
pipeline.add_stage(
stage_name = "Dev",
actions = [
codepipeline_actions.CloudFormationCreateReplaceChangeSetAction(
action_name = "CreateChangeSet",
template_path = codepipeline.ArtifactPath(build_output, "packaged.yaml"),
stack_name = "sam-app",
admin_permissions = True,
change_set_name = "sam-app-dev-changeset",
run_order = 1,
),
codepipeline_actions.CloudFormationExecuteChangeSetAction(
action_name = "Deploy",
stack_name = "sam-app",
change_set_name = "sam-app-dev-changeset",
run_order = 2,
)
]
)
The highlighted code is the new addition:
# pipeline/pipeline_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (core as cdk,
aws_s3 as s3,
aws_codebuild as codebuild,
aws_codecommit as codecommit,
aws_codepipeline as codepipeline,
aws_codepipeline_actions as codepipeline_actions)
class PipelineStack(cdk.Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: cdk.Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
# The code that defines your stack goes here
artifacts_bucket = s3.Bucket(self, "ArtifactsBucket")
# Import existing CodeCommit sam-app repository
code_repo = codecommit.Repository.from_repository_name(self, "AppRepository", "sam-app")
# Pipeline creation starts
pipeline = codepipeline.Pipeline(self, "Pipeline",
artifact_bucket = artifacts_bucket
)
# Declare source code as an artifact
source_output = codepipeline.Artifact()
# Add source stage to pipeline
pipeline.add_stage(
stage_name = "Source",
actions = [
codepipeline_actions.CodeCommitSourceAction(
action_name = "Source",
branch = "main",
output = source_output,
repository = code_repo,
)
]
)
# Declare build output as artifacts
build_output = codepipeline.Artifact()
# Declare a new CodeBuild project
build_project = codebuild.PipelineProject(self, "Build",
environment = codebuild.BuildEnvironment(
build_image = codebuild.LinuxBuildImage.STANDARD_5_0,
),
environment_variables = {
'PACKAGE_BUCKET': codebuild.BuildEnvironmentVariable(value = artifacts_bucket.bucket_name),
},
)
# Add the build stage to our pipeline
pipeline.add_stage(
stage_name = "Build",
actions = [
codepipeline_actions.CodeBuildAction(
action_name = "Build",
project = build_project,
input = source_output,
outputs = [build_output],
)
]
)
# Deploy stage
pipeline.add_stage(
stage_name = "Dev",
actions = [
codepipeline_actions.CloudFormationCreateReplaceChangeSetAction(
action_name = "CreateChangeSet",
template_path = codepipeline.ArtifactPath(build_output, "packaged.yaml"),
stack_name = "sam-app",
admin_permissions = True,
change_set_name = "sam-app-dev-changeset",
run_order = 1,
),
codepipeline_actions.CloudFormationExecuteChangeSetAction(
action_name = "Deploy",
stack_name = "sam-app",
change_set_name = "sam-app-dev-changeset",
run_order = 2,
)
]
)
Deploy the pipeline
On your terminal, run the following commands from within the pipeline directory:
cd ~/environment/sam-app/pipeline
cdk deploy
The CLI might ask you to confirm the changes before deploying, this is because we are giving Admin permissions to the IAM role that deploys our application. This is generally not a bad practice since this role can only be assumed by CloudFormation and not by a human, however, if your organization has a stricter security posture you may want to consider creating a custom IAM deployment role with a fine grain policy.
Trigger a release
Navigate to your pipeline and you will see the Deploy stage has been added, however, it is currently grayed out because it hasn’t been triggered. Let’s just trigger a new run of the pipeline manually by clicking the Release change buttton.